2022年12月08日 10:03
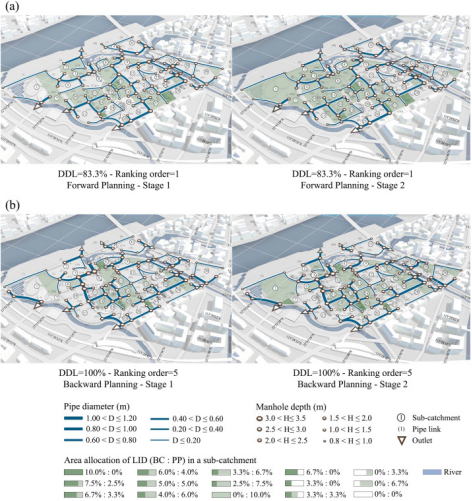
近日,我院风景园林硕士研究生张宇同学作为第一作者于国际顶级期刊《Science of the Total Environment》发表题为《Multi-stage planning of LID-GREI urban drainage systems in response to land-use changes》的研究论文。该研究就灰绿基础设施的多阶段规划建构了实现框架,以香港科技大学(广州)校区空间规划为例,提出了可响应土地利用变化情景下不同时间维度导向的适应性规划路径,为耦合系统的韧性增强路径提供创新方法。该框架可用于支持灰绿基础设施的多阶段规划与投资,有机会为海绵城市及韧性城市建设提供重要的空间决策底座。
该成果的共同作者有研究生刘铭和江知雨,得到“城市声振与关联风险适应性规划”研究团队的培养指导,获广东省自然科学基金(2019A1515010873)、广州市科技项目(202201010431)和2023广州大学-香港科技大学联合研究合作基金的共同资助。
《Science of the Total Environment》为中科院一区顶级期刊,2022年影响因子为10.753。该成果的发表为我校风景园林硕士科研工作的新突破。张宇同学在校期间已发表SCI论文4篇,其中3篇为中科院一区顶级期刊,总影响因子接近40。

张 宇
2020级风景园林研究生
[1] Multi-stage planning of LID-GREI urban drainage systems in response to land-use changes [J]. Science of The Total Environment, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160214.
[2] Designing coupled LID-GREl urban drainage systems: Resilience assessment and decision-making framework [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 834: 155267.
[3] A Bayesian Decision Model for Optimum Investment and Design of Low-Impact Development in Urban Stormwater Infrastructure and Management [J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2021: 462.
[4] Life-cycle cost analysis and resilience consideration for coupled grey infrastructure and low-impact development practices [J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 75: 103358.
[5] Technological and operational resilience in multi-objective optimization of coupled green-grey stormwater infrastructure [J] Earth's Future, Under review.
[6] A comprehensive decision-making framework for Grey-Green coupled stormwater system in response to climate change [J] Water research, Major revision.
[7] Assessing hydrological performance for optimized integrated grey-green infrastructure in response to climate change based on shared socio-economic pathways [J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, Under review.
[8] A multi-objective optimization integrating life cycle cost and systematic resilience for planning of holistic grey-green stormwater infrastructure [J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, Under review.
Funding: The Graduate Student Innovation Ability Training Funding Program of Guangzhou University [grant number 2021GDJC-M38].

刘 铭
2020级风景园林研究生
[1] Multi-stage planning of LID-GREI urban drainage systems in response to land-use changes [J]. Science of The Total Environment, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160214.
[2] Designing coupled LID-GREl urban drainage systems: Resilience assessment and decision-making framework [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 834: 155267.
[3] Technological and operational resilience in multi-objective optimization of coupled green-grey stormwater infrastructure [J] Earth's Future, Under review.
[4] A comprehensive decision-making framework for Grey-Green coupled stormwater system in response to climate change [J] Water research, Major revision.
[5] Assessing hydrological performance for optimized integrated grey-green infrastructure in response to climate change based on shared socio-economic pathways [J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, Under review.
[6] A multi-objective optimization integrating life cycle cost and systematic resilience for planning of holistic grey-green stormwater infrastructure [J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, Under review.
Funding: 2022 Guangzhou University full-time postgraduate "Guangzhou Research" project.

江 知雨
2021级风景园林研究生
[1] Multi-stage planning of LID-GREI urban drainage systems in response to land-use changes [J]. Science of The Total Environment, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160214.
[2] A multi-objective optimization integrating life cycle cost and systematic resilience for planning of holistic grey-green stormwater infrastructure [J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, Under review.
(供稿人:钟浩瀚)
下一篇:学院主持的重要学术科研项目